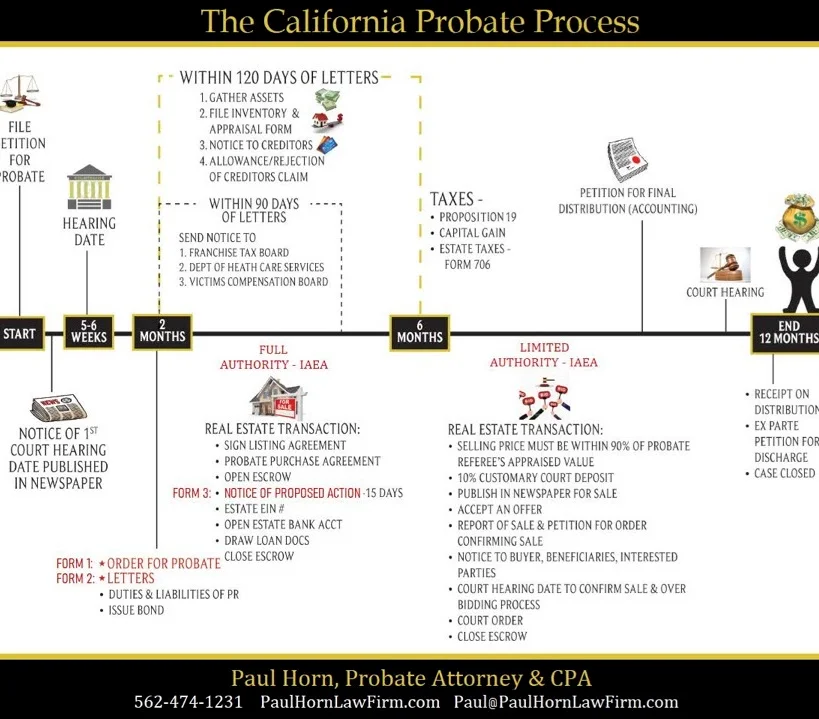
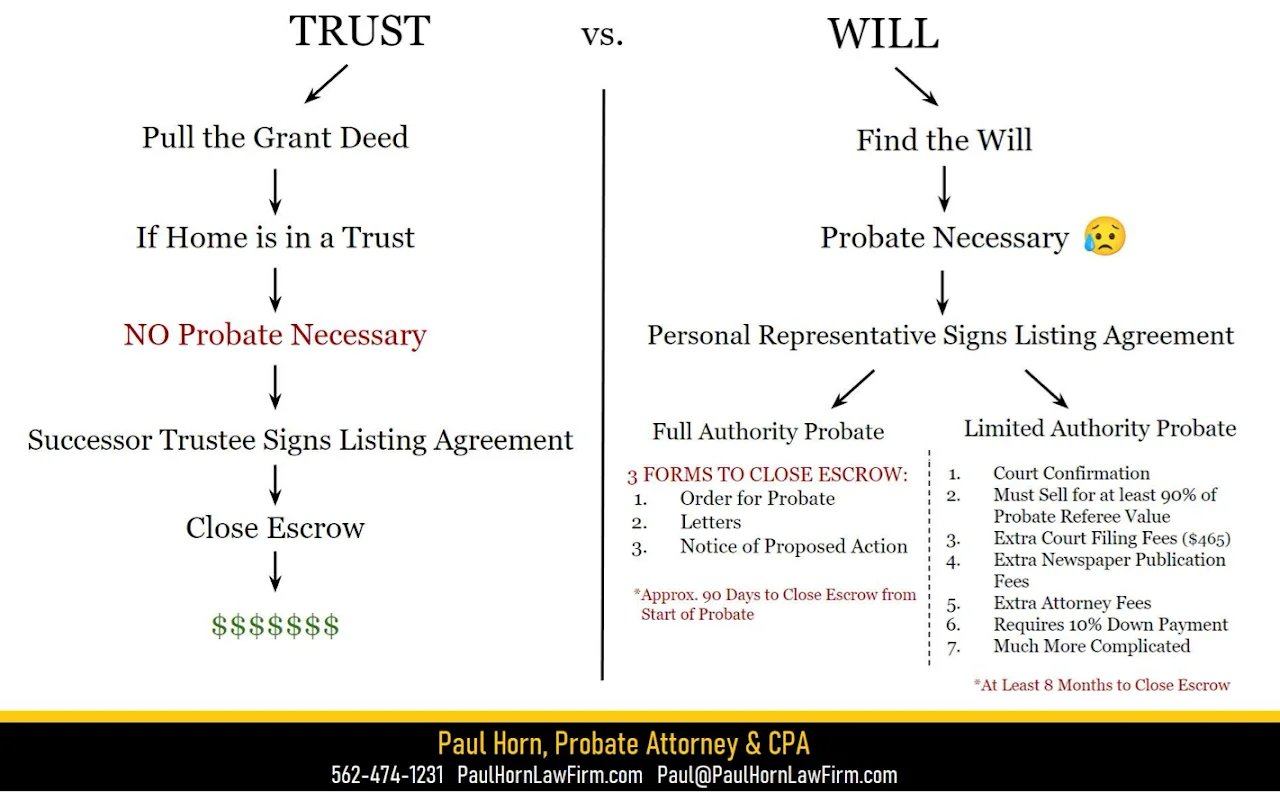
Probate is a court-sanctioned process that allows the transfer of a deceased person’s property to the living heirs. Probate proceedings serve many purposes such as gathering and safeguarding assets, paying all legitimate creditors, and distributing the Estate’s assets to the appropriate heirs.
A probate proceeding serves various functions, including the collection and protection of the deceased person’s assets, settling the legitimate debts owed by the deceased, and allocating the estate’s assets to the appropriate beneficiaries. Probate is a court-approved procedure that facilitates the transfer of the deceased individual’s property to the living heirs. To draw a parallel in real estate terms, when selling a property, the homeowner typically signs a deed to transfer ownership to the buyer. However, if the homeowner has passed away, the court must appoint a Personal Representative, who could be an executor designated in the will/trust, or an administrator in the absence of a will. This appointed individual possesses the legal authority to sign the deed, effecting the transfer of the house to the buyer, all under the court’s supervision.In essence, probate acts as a form of “title clearance” for both real and personal property, as these assets are initially registered under the deceased individual’s name. Consequently, the court appoints a Personal Representative to act on behalf of the deceased person
You will need a copy of the trust to move forward with selling the property. SEARCH THE HOUSE! . Unlike recorded title documents in the county archives, Trusts are not recorded. You will need to locate a copy of the trust. Ask the family attorney or CPA that might have have worked on the case.
Provided by Paul Horn, Probate Attorney and CPA